Dental Caries in Children – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
Table of Contents
Dental caries, commonly known as tooth decay or cavities, can affect children just as it can affect adults. Here’s some information on dental caries in children, including symptoms, causes, and treatment, as well as a mention of nursing bottle caries, a specific form of tooth decay in infants.
Dental Caries in Children:
Symptoms:
- Toothache: A child may experience tooth pain, particularly while eating or drinking.
- Sensitivity: Teeth may become sensitive to hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and drinks.
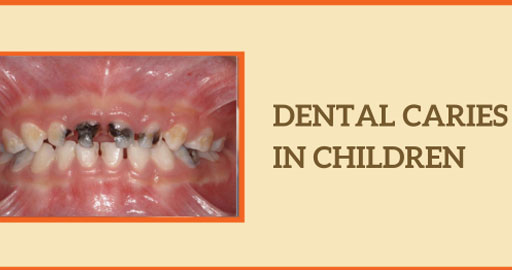
- Visible Discoloration: White, brown, or black spots or stains on the teeth may be visible.
- Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath or an unpleasant taste in the mouth may be present.
- Chewing Difficulty: Children might have trouble chewing their food due to pain or discomfort.
- Swelling or Pus: In severe cases, there may be swelling or the presence of pus near the affected tooth.
Causes:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to the accumulation of plaque, which contains bacteria that produce acids that damage the enamel.
- Diet: Frequent consumption of sugary snacks and drinks can increase the risk of dental caries.
- Bacterial Infection: Streptococcus mutans is a common bacterium involved in tooth decay.
- Lack of Fluoride: Insufficient fluoride exposure can weaken tooth enamel’s resistance to acids.
- Genetics: Some children may be more genetically predisposed to dental caries.
Treatment :
- Dental Fillings: Dentists can fill cavities with materials like amalgam or composite resin.
- Fluoride Treatments: Professional fluoride applications can help strengthen tooth enamel.
- Dental Crowns: In more severe cases, dental crowns may be necessary to restore damaged teeth.
- Pulp Therapy: If the decay reaches the inner pulp of the tooth, root canal treatment may be needed.
- Extraction: In cases of severe decay, a tooth may need to be removed.
Prevention:
- Oral Hygiene: Teach children to brush and floss regularly.
- Balanced Diet: Encourage a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and limited sugary snacks.
- Fluoride: Ensure access to fluoride through toothpaste, drinking water, or dental treatments.
- Regular Dental Checkups: Schedule regular dental visits for cleanings and checkups.
Nursing Bottle Caries:
Nursing bottle caries, also known as baby bottle tooth decay or early childhood caries, is a specific form of dental caries that affects infants and young children. It is primarily caused by prolonged exposure of a child’s teeth to sugary liquids, such as milk, formula, or fruit juice, especially when they fall asleep with a bottle in their mouth. The sugars in these liquids provide a food source for bacteria, leading to tooth decay.
Symptoms of nursing bottle caries can include visible decay, pain, and difficulty eating. Prevention dentistry includes avoiding bedtime or naptime bottle use, cleaning a baby’s gums with a soft cloth, and introducing a regular drinking cup as early as possible.
In summary, dental caries in children is a common oral health issue with identifiable symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Preventive measures, including proper oral hygiene and dietary choices, are essential in reducing the risk of tooth decay in children. Nursing bottle caries is a specific concern for infants and can be prevented by avoiding prolonged exposure to sugary liquids. Regular dental checkups are crucial to catch and address dental caries in children at an early stage. By: Dr. Nayanika Batra
Leave a Reply
Leave a Reply