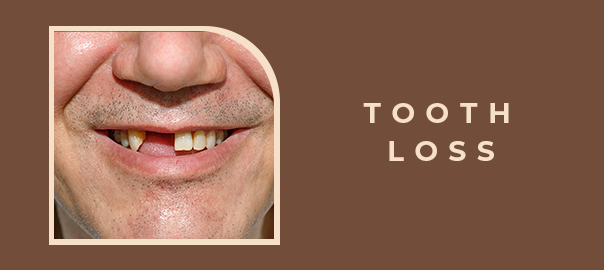
Tooth Loss – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
Tooth loss is a prevalent dental condition that can significantly impact a person’s oral health and overall well-being. Whether caused by decay, trauma, or other underlying factors, tooth loss requires attention and appropriate treatment to restore oral function and prevent further complications. This article explores the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for tooth loss, offering insights into maintaining optimal oral health.
Symptoms of Tooth Loss
- 1. Loose or wobbly teeth.
- 2. Pain or discomfort while chewing.
- 3. Gum inflammation or tenderness.
- 4. Difficulty biting or chewing properly.
- 5. Visible gaps between teeth.
- 6. Changes in the alignment of teeth.
Causes of Tooth Loss
- 1. Poor oral hygiene: Inadequate brushing, flossing, and regular dental check-ups can lead to decay and gum disease, ultimately resulting in tooth loss.
- 2. Gum disease (periodontitis): Untreated gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, causing damage to the gums and supporting structures of the teeth.
- 3. Tooth decay (cavities): Bacteria in the mouth produce acids that erode tooth enamel, leading to decay and eventual tooth loss if not treated promptly.
- 4. Trauma or injury: Accidents, sports injuries, or physical trauma to the mouth can cause tooth fractures or avulsion, resulting in tooth loss.
- 5. Genetics: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to gum disease or enamel defects, increasing their risk of tooth loss.
- 6. Poor nutrition: A diet lacking essential nutrients, especially calcium and vitamin D, can weaken teeth and bones, contributing to tooth loss over time.
- 7. Smoking and tobacco use: Tobacco products increase the risk of gum disease and interfere with the body’s ability to heal, accelerating tooth loss.
- 8. Medical conditions: Systemic diseases like diabetes or osteoporosis can affect oral health and increase susceptibility to tooth loss.
Treatment Options for Tooth Loss
- 1. Dental implants: Titanium posts surgically implanted into the jawbone serve as artificial tooth roots, providing a stable foundation for dental crowns or bridges.
- 2. Dentures: Removable prosthetic devices designed to replace missing teeth and restore oral function and aesthetics.
- 3. Dental bridges: Custom-made prosthetic teeth anchored to adjacent natural teeth or implants to bridge the gap created by missing teeth.
- 4. Gum disease treatment: Scaling and root planning, antibiotic therapy, and surgical interventions may be necessary to manage gum disease and prevent further tooth loss.
- 5. Tooth extraction: In cases of severe decay, trauma, or overcrowding, extraction may be necessary to preserve oral health and prevent complications.
- 6. Orthodontic treatment: Braces or clear aligners can correct misaligned teeth and bite issues, reducing the risk of tooth loss due to malocclusion.
Prevention is Key
Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, prevents tooth loss. Additionally, adopting a balanced diet, avoiding tobacco use, and addressing underlying medical conditions can help safeguard against oral health problems.
Conclusion
Tooth loss can have significant implications for oral health and quality of life, but timely intervention and appropriate treatment can help restore function and aesthetics. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for tooth loss, individuals can take proactive steps to preserve their oral health and well-being for years. Remember, a healthy smile starts with good oral hygiene and regular dental care.
DISCLAIMER:Please note that the prices mentioned on this page: (a) present a range (depending upon the severity of the dental condition, the technology used in treatment, type of dental products used, etc.); (b) are true as on the date of this page and may change on a later date, in accordance with the standard company policy; (c) may be subject to standard aberrations or generalizations on account of the use of AI in general Google/internet search by you.Leave a Reply
Leave a Reply
Explore More Similar Posts
Explore More Blogs


Leave a Reply