Tooth Hypermobility – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
Table of Contents
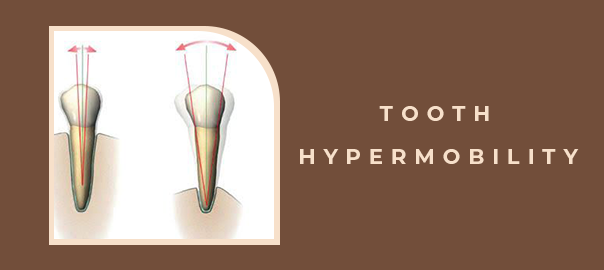
Tooth hypermobility, or loose teeth or tooth mobility, is when teeth feel loose or move within the sockets. Movement of the tooth can indicate issues that require attention. This article will explore the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for tooth hypermobility.
Symptoms of Tooth Hypermobility
- 1. One of the primary symptoms of tooth hypermobility is loose teeth. Individuals may notice that their teeth feel unstable or move quickly when pressure is applied, such as chewing or brushing.
- 2. Patients with tooth hypermobility may experience pain or discomfort, especially when biting down or chewing. This discomfort can vary from mild to severe, depending on the extent of the hypermobility and any accompanying dental issues.
- 3. Tooth hypermobility can also lead to gum recession, where the gums pull away from the teeth, exposing more of the tooth’s surface. This can cause sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures and increase the risk of tooth decay.
Causes of Tooth Hypermobility
- 1. Genetics play a significant role in determining the strength and stability of teeth. Some individuals may inherit weaker tooth structures or predispositions to conditions such as gum disease, which can contribute to tooth hypermobility.
- 2. Trauma or injury to the mouth, such as accidents or sports injuries, can damage the ligaments and tissues that support the teeth, leading to increased mobility.
- 3. Inadequate dental care, including irregular brushing and flossing, and skipping routine dental check-ups, can contribute to tooth decay, gum disease, and ultimately, tooth hypermobility.
Treatment Options
- 1. Dental Splints or Braces: Dentists may recommend dental splints or braces in more severe cases to stabilize the teeth and prevent further movement. These devices help redistribute biting forces and support the surrounding structures.
- 2. Surgery: In rare instances where other treatments have been unsuccessful, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair damaged ligaments or reposition the teeth.
Preventive Measures
- 1. Good Oral Hygiene: Maintaining good oral hygiene habits, including brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and using mouthwash, can help prevent tooth decay and gum disease, reducing the risk of tooth hypermobility.
- 2. Regular Dental Checkups: Routine dental check-ups are essential for early detection and intervention of dental issues, including tooth hypermobility. Dentists can monitor changes in the teeth and gums and provide timely treatment as needed.
Conclusion
Tooth hypermobility can significantly impact an individual’s oral health and quality of life. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options available, patients can take proactive steps to manage their condition and maintain a healthy smile.
FAQs
1. Can tooth hypermobility be reversed?
Tooth hypermobility can be managed and treated, but complete reversal may not always be possible, depending on the underlying causes and severity of the condition.
2. Is tooth hypermobility common?
Tooth hypermobility is relatively common and can affect people of all ages, but it is more prevalent in individuals with certain genetic predispositions or underlying dental issues.
3. Can tooth hypermobility cause tooth loss?
If left untreated, severe tooth hypermobility can lead to tooth loss due to damage to the supporting structures and increased susceptibility to decay and gum disease.
4. Are there any home remedies for tooth hypermobility?
While practicing good oral hygiene is essential, home remedies alone are not sufficient to treat tooth hypermobility. It’s important to seek professional dental care for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
5. How can I prevent tooth hypermobility?
Preventive measures such as maintaining good oral hygiene, wearing mouthguards during sports activities, and avoiding habits that can damage the teeth, such as nail-biting or using teeth as tools, can help reduce the risk of tooth hypermobility.