Dental Pulpitis – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
Table of Contents
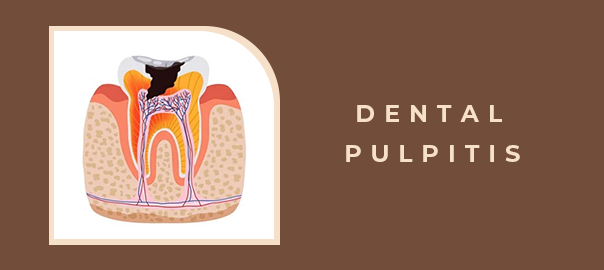
Dental health plays a crucial role in our overall well-being, and one common dental issue many individuals face is dental pulpitis. This condition involves dental pulp inflammation, which is the innermost part of the tooth containing nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissues. This blog will delve into the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for dental pulpitis to help you better understand and manage this oral health concern.
Symptoms
- 1. Toothache: A persistent toothache is the most common and noticeable symptom of dental pulpitis. This pain can range from mild to severe and may be triggered by hot or cold foods, sweets, or even air.
- 2. Sensitivity: Individuals with dental pulpitis often experience increased sensitivity to temperature changes, making consuming hot or cold beverages uncomfortable.
- 3. Swelling and Redness: In some cases, the affected tooth and surrounding gums may exhibit swelling and redness. This indicates an inflammatory response within the tooth.
- 4. Pain while Chewing: Dental pulpitis can lead to discomfort and pain while chewing or biting down. This pain may be localized to the affected tooth.
Causes
- 1. Untreated Cavities: The most common cause of dental pulpitis is untreated cavities or dental caries. When bacteria penetrate the enamel and dentin layers of the tooth, they can reach the pulp, leading to inflammation.
- 2. Dental Trauma: Accidents or injuries to the teeth can result in pulpitis. The trauma can damage the pulp directly or indirectly, causing inflammation over time.
- 3. Cracked or Fractured Teeth: Cracks or fractures in the teeth can expose the dental pulp to bacteria, leading to infection and inflammation.
- 4. Repetitive Dental Procedures: Multiple dental procedures, especially if they involve drilling or manipulation of the tooth, can increase the risk of pulpitis.
Treatment
- 1. Root Canal Therapy: This is a standard and effective treatment for dental pulpitis. It involves removing the infected pulp, cleaning and disinfecting the root canal, and sealing it to prevent further infection.
- 2. Medication: Pain relievers and antibiotics may be prescribed to manage pain and combat bacterial infection. Over-the-counter pain relievers can also provide temporary relief.
- 3. Dental Restoration: In cases where dental caries or fractures are the culprits, the dentist may recommend dental restorations such as fillings or crowns to repair and protect the affected tooth.
- 4. Tooth Extraction: In severe cases where the damage is extensive and irreparable, the tooth may need to be extracted to prevent the spread of infection.
Prevention
- 1. Good Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups are essential to prevent cavities and maintain oral health.
- 2. Protective Gear: Use appropriate protective gear during sports activities to minimize the risk of dental trauma.
- 3. Prompt Dental Care: Seek prompt dental care for any signs of tooth decay, damage, or persistent toothache to prevent the progression to pulpitis.
Conclusion:
Dental pulpitis is a dental condition that requires timely attention and professional intervention. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for optimal oral health. If you experience persistent tooth pain or any other symptoms mentioned, it is advisable to consult with your dentist promptly for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups are vital to preventing dental pulpitis and other oral health issues.
DISCLAIMER:Please note that the prices mentioned on this page: (a) present a range (depending upon the severity of the dental condition, the technology used in treatment, type of dental products used, etc.); (b) are true as on the date of this page and may change on a later date, in accordance with the standard company policy; (c) may be subject to standard aberrations or generalizations on account of the use of AI in general Google/internet search by you.Leave a Reply
Leave a Reply
Explore More Similar Posts
Explore More Blogs


Leave a Reply