Dental Hypocalcification – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
Table of Contents
Maintaining good oral health is essential for overall well-being, and one common dental condition that can affect both children and adults is hypocalcification of teeth. This condition can lead to various dental issues, and it’s essential to understand its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options. This blog will delve into the world of hypocalcification, providing you with medically accurate information to help you better comprehend this dental concern.
What is Hypocalcification of Teeth?
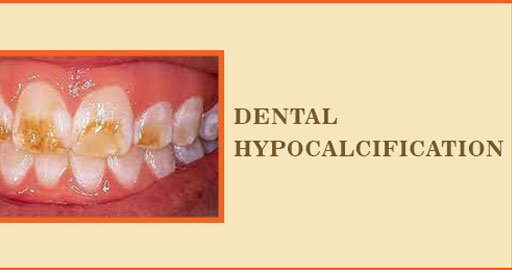
Hypocalcification of teeth, often called enamel hypocalcification, is a dental condition characterized by insufficient mineralization of tooth enamel. Tooth enamel is the outermost layer of your teeth and plays a crucial role in protecting your teeth from decay and damage. When enamel doesn’t mineralize properly, it can result in weaker teeth, making them more susceptible to dental issues.
Causes of Hypocalcification
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Insufficient intake of essential minerals, such as calcium and phosphate, can contribute to hypocalcification during tooth development.
- Genetics: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to enamel defects, which can result in hypocalcification.
- Premature Birth or Low Birth Weight: Children born prematurely or with low birth weight are at a higher risk of developing enamel defects, including hypocalcification.
- Fluorosis: Excessive fluoride exposure during tooth development can cause enamel hypocalcification. This is often due to consuming fluoride-rich water or using fluoride-containing dental products excessively.
Symptoms of Hypocalcification
Hypocalcification can manifest with various symptoms, which may include:
- White or yellowish spots on the teeth.
- Sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures
- Rapid tooth decay.
- Weakened enamel that chips or breaks easily.
Diagnosis of Dental Hypocalcification
Detecting dental hypocalcification involves various diagnostic methods to assess the extent and severity of enamel mineralization defects. Dentists use a combination of visual examination, dental imaging techniques, and sometimes laboratory tests to diagnose this condition accurately. Below are standard diagnostic methods for detecting dental hypocalcification:
- Visual Examination: Dentists typically begin by visually inspecting the teeth for any visible signs of hypocalcification, such as white or yellowish spots, enamel discoloration, or areas of enamel that appear chalky or porous. While visual examination provides valuable initial insights, it may not always detect subtle or early-stage hypocalcification.
- Dental Imaging: X-rays, intraoral cameras, and other dental imaging techniques allow dentists to visualize enamel defects, assess the extent of mineralization abnormalities, and identify areas of enamel demineralization not visible to the naked eye.
Treatment Options
Understanding how each treatment option works, along with their benefits, risks, and effectiveness, is crucial for managing dental hypocalcification effectively:
Dental Bonding: Dental bonding involves applying a tooth-colored resin to the affected teeth, which bonds to the enamel surface, filling in gaps and strengthening weakened areas.
- Benefits: Dental bonding is minimally invasive, aesthetically pleasing, and can improve tooth strength and appearance.
- Risks: Bonding may need to be replaced over time and may not be suitable for extensive enamel defects.
- Effectiveness: Bonding can effectively restore the appearance and function of teeth affected by mild to moderate hypocalcification.
Dental Crowns: Dental crowns, also known as caps, are tooth-shaped prosthetic devices that cover the entire visible portion of a tooth, providing protection and support to weakened enamel.
- Benefits: Crowns offer durable, long-lasting protection for severely affected teeth and can enhance both function and aesthetics.
- Risks: Crown placement requires tooth preparation and may involve the removal of healthy enamel. There’s also a risk of complications such as decay or gum disease around the crown margins.
- Effectiveness: Crowns are highly effective for restoring severely hypocalcified teeth, providing strength and stability.
Fluoride Treatment: Topical fluoride applications, such as gels, varnishes, or rinses, can help remineralize enamel, strengthen teeth, and reduce the risk of decay.
- Benefits: Fluoride treatment is non-invasive, cost-effective, and readily available. It can also benefit overall oral health by preventing cavities.
- Risks: Excessive fluoride intake can lead to fluorosis, and some individuals may be allergic to fluoride or sensitive to its taste.
- Effectiveness: Fluoride treatment effectively manages early-stage hypocalcification and prevents further enamel demineralization.
Lifestyle and Dietary Changes: Adopting a balanced diet rich in essential minerals, maintaining good oral hygiene, and limiting fluoride exposure can help prevent and manage hypocalcification.
- Benefits: Lifestyle and dietary changes promote oral health and complement other treatment strategies.
- Risks: Compliance with dietary recommendations may be challenging, and nutritional modifications alone may not address severe hypocalcification.
- Effectiveness: When combined with other treatment modalities, lifestyle, and dietary changes can support enamel remineralization and reduce the risk of enamel defects.
Regular Dental Check-ups:Routine dental examinations allow dentists to monitor the progression of hypocalcification, identify any complications or emerging issues, and adjust treatment plans as needed.
- Benefits: Regular dental check-ups facilitate early detection and intervention, helping prevent complications associated with untreated hypocalcification.
- Risks: Delayed or infrequent dental visits may result in undetected enamel defects and the progression of dental problems.
- Effectiveness: Regular dental check-ups are essential for maintaining oral health and optimizing treatment outcomes for individuals with hypocalcification.
Preventing Hypocalcification
To prevent hypocalcification, consider the following
- Maintain a balanced diet with sufficient calcium and phosphate.
- Control fluoride intake, especially in young children.
- Practice good oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing.
- Attend regular dental check-ups.
Conclusion
Dental Hypocalcification of teeth is a common dental issue that can significantly impact oral health. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for early detection and management. If you suspect you or your child may have hypocalcification, it’s crucial to consult a dentist at Clove Dental for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan. You can enjoy a healthier and brighter smile for years by taking proactive steps to address
DISCLAIMER:Please note that the prices mentioned on this page: (a) present a range (depending upon the severity of the dental condition, the technology used in treatment, type of dental products used, etc.); (b) are true as on the date of this page and may change on a later date, in accordance with the standard company policy; (c) may be subject to standard aberrations or generalizations on account of the use of AI in general Google/internet search by you.Leave a Reply
Leave a Reply
Explore More Similar Posts
Explore More Blogs


Leave a Reply