Oral Cancer – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
Oral cancer is a grave health risk. It can invade your lips, tongue, cheeks, and throat. Spotting it early and understanding the disease is key. These can improve treatment and outcomes.
This post will guide you through oral cancer. It will cover signs, reasons, treatment options, and tips to avoid it.
What Is Oral Cancer?
Mouth cancer, or oral cancer, occurs when cells grow wildly in the mouth or throat. It can pop up in various places, such as the lips, gums, tongue, top, bottom, even the throat’s back! If mouth cancer isn’t stopped early, it can spread to other body parts. So, finding it fast is critical.
Symptoms of Mouth Cancer
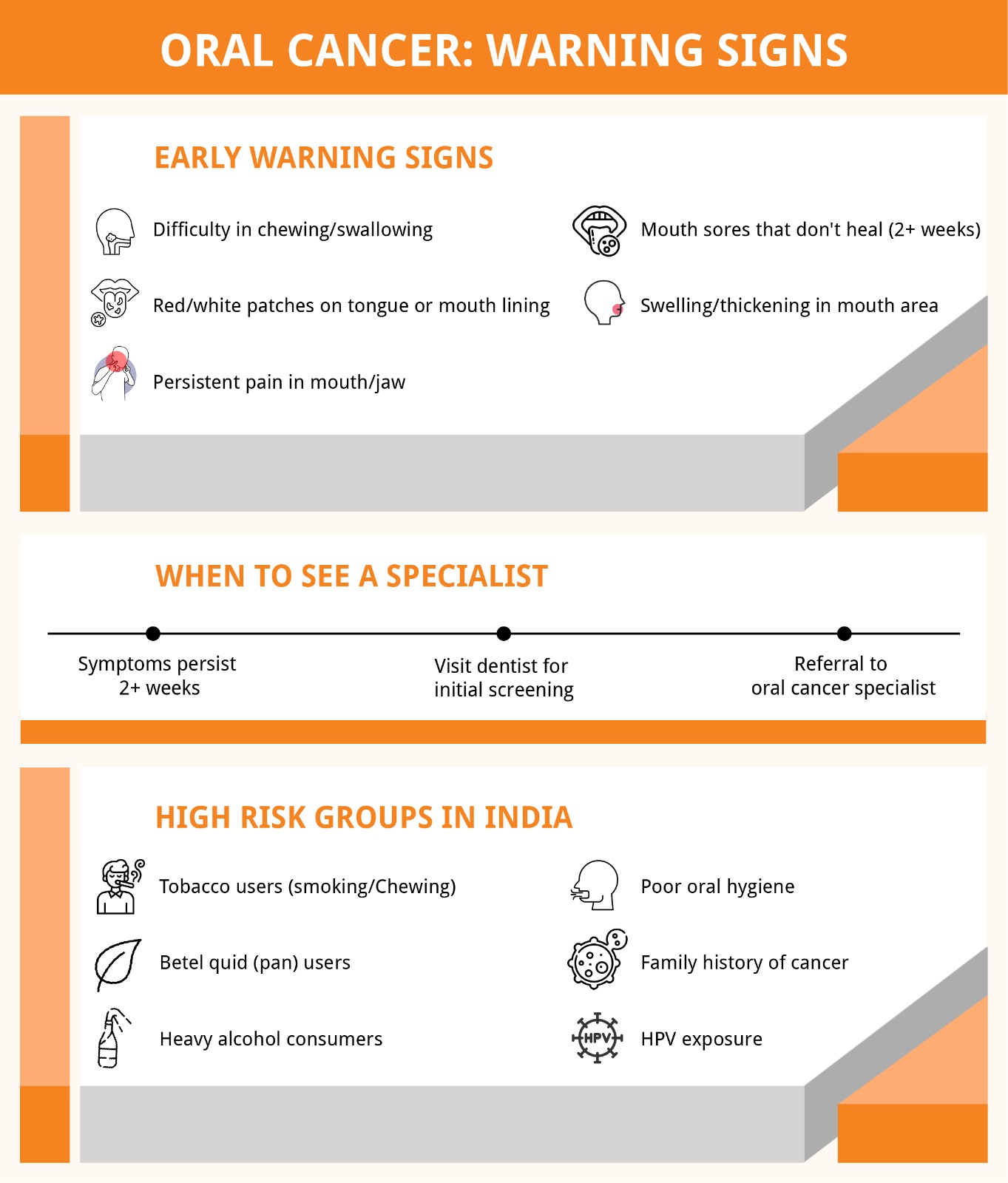
Awareness of mouth cancer symptoms can help in early detection and treatment. Some common signs include:
Enduring Mouth Sores: Sores or ulcers in the mouth not healing over two weeks.
Odd Red or White Spots: Unique red or white spots appearing on the tongue, gums, or inner cheeks.
Chewing and Swallowing Troubles: A sensation of an object lodged in the throat or problems chewing food.
Continuous Throat Discomfort: A lingering sore throat resisting standard remedies.
Unjustified Discomfort: Pain or unease in the mouth, face, neck, or jaw.
Shaky Teeth: Teeth loosening up unexpectedly without a clear dental reason.
Bulges or Lumps: A rise in the jaw, neck, or mouth potentially triggering discomfort or a numb feel.
Altered Voice: Changes in the voice or having a raspy tone.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional or dentist promptly.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing oral cancer. Here are the most common causes:
Using Tobacco: Regular smoking and the use of spit tobacco rank high as oral cancer causes.
Drinking Alcohol: Drinking a lot, particularly mixed with tobacco, ramps up the risk significantly.
HPV: Particular types of HPV have a strong connection to cancers of the mouth and throat.
Sun Exposure: Spending a long time in the sun without safeguarding can cause lip cancer.
Lack of Oral Care: Constant irritation from bad dental upkeep and gum problems can bring about oral cancer.
Family History: If your family has had oral or other cancers, your risk could go up.
Diagnosis and Screening for Oral Cancer
Early diagnosis plays a crucial role in the successful treatment of oral cancer. Diagnosis typically involves:
Check-up: The doctor or dentist looks all around the mouth. They’re looking for sores, lumps, or irregular spots.
Tissue Sample: If something odd is spotted, they’ll take a little bit of that area. It goes to a lab for testing.
Pictures of the Inside: Sometimes they need to see deeper. Dental X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs can show if the cancer has moved.
HPV Check: In certain situations, an HPV test might be suggested. This helps to spot any related threats.
Regular dental check-ups can help identify signs of oral cancer early, even before symptoms appear.
Treatments for Oral Cancer
Treatment options for oral cancer depend on the stage and location of the disease. Common treatments include:
Surgery: Doctors get rid of the tumour, sometimes affecting lymph nodes. They reconstruct afterwards for looks and function.
Radiation: Cancer-killing high-energy rays. Used alone or with surgery for cases at early stages.
Chemo: Drugs stop cancer cells from growing. Used with radiation for serious cases.
Targeted Therapy: Targets molecules involved in cancer’s growth, less harm to healthy cells.
Immunotherapy: Boosting your immune system to beat cancer. A new type of treatment giving hope to some patients.
How to Prevent Oral Cancer
While not all cases of oral cancer can be prevented, certain lifestyle changes can significantly lower the risk:
Stay Away from Tobacco, Control Alcohol: Do not smoke and drink moderately.
Follow Dental Care Regimen: Brush and floss daily, and have routine dentist visits to keep great oral health.
Safeguard yourself from the Sun: Apply SPF lip balms and lessen long sun exposure.
Get Immunized: HPV shots can cut down chances of related cancer types.
Stick to Healthy Eating: Consume a variety of fruits and vegetables, and maintain a nutritious balance in your diet.
Oral Cancer Awareness in India
In the whole world, India sees a lot of oral cancer cases. This is mostly because many people there use tobacco and betel quid (areca nut). To fight this big health problem, we need things like the public telling people about it, checking for it early, and teaching people to live healthier. Going to the dentist often and doing something about symptoms quickly can save lives.
FAQs About Oral Cancer
1. What are the first signs of cancer in the mouth?
Non-healing sores, red or white patches, and unexplained lumps are common early signs.
2. Can mouth cancer be cured?
Yes, if detected early, oral cancer has a high survival rate with appropriate treatment.
3. How fast does mouth cancer spread?
The speed varies, but early-stage oral cancer typically spreads slower than advanced cases.
4. What does stage 1 mouth cancer look like?
Stage 1 oral cancer often appears as small, localized sores or patches without noticeable pain.
Final Thoughts
Catching oral cancer early can stop it in its tracks and lead to successful treatment. Regular dentist check-ups, living healthily, and curbing habits like drinking and smoking are key. See something odd in your mouth that won’t quit? Get medical help ASAP. The key to stopping oral cancer is being aware and taking fast action.
Leave a Reply
Leave a Reply
Explore More Similar Posts
Explore More Blogs


Leave a Reply