Gum Disease – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
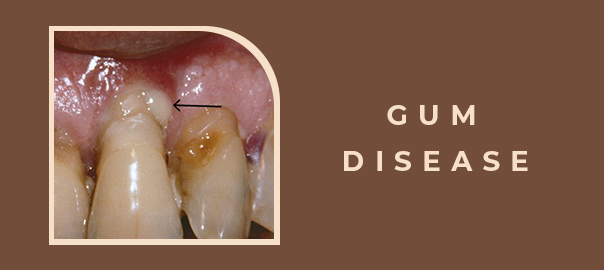
Periodontal or gum disease is among the commonest dental or oral diseases throughout most populations in the world. Symptoms do not appear mostly until advanced stages of the disease. It is therefore considered a silent intruder due to the fact of its action on the gums and teeth, which may result in grave complications when unchecked. In this blog, we look at symptoms, causes, and available treatments for gum disease as a means of raising greater awareness of this often-overlooked aspect of oral hygiene.
Symptoms of Gum Disease:
- 1. Gums that Bleed: One symptom that is rather considered an actual sign of gum disease is bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing. The healthy gums must not bleed; hence, in case they do, that would serve as a sign to be taken into notice.
should not bleed, so if you notice blood, it’s crucial to pay attention. - 2. Swollen or Sensitive Gums: At times, accompanied by progressive action from the disease, there may be inflammation and tenderness, which leaves the gums swollen and red.
- 3. Bad Breath: Recurring bad breath may also point to the presence of the disease. Receding Gums: Advanced cases of gum disease may picture recession of gums from the tooth structure, development of gum pockets, which are seemingly a habitat for bacteria to reside in. Loose or Shifting Teeth: In advanced stages, support structures of teeth may weaken, and teeth become mobile or shift.
Causes of Gum Disease:
- 1. Poor oral hygiene leads to incomplete brushing and flossing, and leaves plaque-a sticky film of bacteria-on the teeth inflaming the gum.
- 2. Tobacco use-a kind of smoking and tobacco chewing-facilitates the development and advancement of gum diseases.
- 3. Genetics-as with any other disease, it can also result in one person easily being caught by dental problems, even when all oral hygiene practices are followed.
- 4. Medical conditions that predispose an individual to this disease are diseases such as diabetes and autoimmune disorders.
- 5. Poor nutrition decreases immunity and hence leads to issues in oral health
Treatment Modalities:
- 1. Professional Dental Cleaning: This normally cleans the teeth to remove plaque and tartar that have formed in order to prevent further disease of the gums.
- 2. Scaling and Root Planing: This is a nonsurgical procedure for deep cleaning, which involves removal of plaque and tartar from under the gum line, smoothing root surfaces to enhance healing.
- 3. Antibiotics: These are supposed to keep bacterial infection at bay by applying antibiotics either in targeted areas or for general use.
- 4. Surgical Interventions: Advanced stages may necessitate the replacement of destroyed tissues with flap surgery or bone and tissue grafts.
- 5. Changes in Life Habits: Quitting smoking and proper oral hygiene have been assumed as the essentials for the prevention and treatment of periodontal diseases assisted by a healthy life.
Conclusion:
This is the unsung yet common threat to oral health. Symptom identification, knowledge of its etiology and early treatment will amount to healthy gums and a smile worth flashing. Regular dental consultations, and oral hygiene adherence to the main features compose the prevention and control of the disease to ensure optimum oral health throughout one’s life.
DISCLAIMER:Please note that the prices mentioned on this page: (a) present a range (depending upon the severity of the dental condition, the technology used in treatment, type of dental products used, etc.); (b) are true as on the date of this page and may change on a later date, in accordance with the standard company policy; (c) may be subject to standard aberrations or generalizations on account of the use of AI in general Google/internet search by you.Leave a Reply
Leave a Reply
Explore More Similar Posts
Explore More Blogs


Leave a Reply