Gingival Hyperplasia – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
Table of Contents
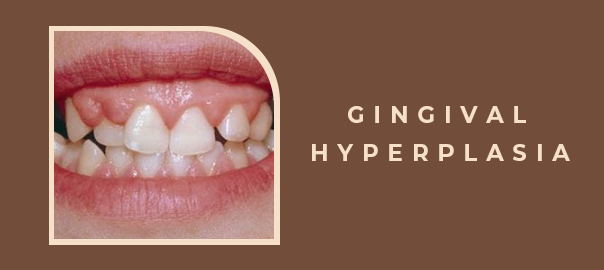
Gingival hyperplasia, also known as gingival overgrowth or gum enlargement, is a dental condition characterized by the abnormal overgrowth of the gingival tissues. This condition can affect individuals of all ages and can lead to various complications if left untreated. In this blog post, we will explore the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for gingival hyperplasia.
Symptoms
- 1. Enlarged Gums: The most obvious symptom of gingival hyperplasia is the enlargement of the gums. This can lead to a swollen, puffy appearance of the gums, making it difficult to maintain proper oral hygiene.
- 2. Bleeding Gums: Overgrown gums are more prone to bleeding, especially during brushing or flossing. This can contribute to the development of gingivitis and other oral health issues.
- 3. Discomfort or Pain: Some individuals with gingival hyperplasia may experience discomfort or pain in the affected areas, particularly when chewing or biting.
- 4. Changes in Tooth Alignment: In severe cases, the overgrowth of gum tissue can cause changes in tooth alignment, leading to issues such as malocclusion.
Causes
- 1. Medications: Gingival hyperplasia is often associated with certain medications, such as anticonvulsants, calcium channel blockers, and immunosuppressants. These drugs can interfere with the normal growth and maintenance of gum tissues.
- 2. Genetics: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to developing gingival hyperplasia. If a family member has experienced this condition, there may be an increased risk for others in the family.
- 3. Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate oral hygiene practices can contribute to the development of gingival hyperplasia. Plaque and bacteria buildup can irritate the gums and trigger an overgrowth response.
- 4. Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause, can influence gum health and contribute to the development of gingival hyperplasia.
Treatment Options
- 1. Improved Oral Hygiene: Maintaining proper oral hygiene is crucial in managing gingival hyperplasia. This includes regular brushing, flossing, and professional dental cleanings to reduce plaque and bacteria.
- 2. Medication Adjustment: If the condition is medication-induced, consulting with a dentist to adjust the dosage or switch to an alternative medication may be recommended.
- 3. Surgical Intervention: In severe cases, surgical procedures such as gingivectomy (removing excess gum tissue) may be necessary to restore a normal gum line and improve oral health.
Conclusion:
Gingival hyperplasia is a condition that requires prompt attention to prevent complications and maintain good oral health. If you suspect you have gingival hyperplasia or notice any of the symptoms mentioned, it is essential to consult with a dentist or healthcare professional for a thorough examination and appropriate treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. Early intervention and proper management can help restore a healthy gum profile and prevent further complications.
DISCLAIMER:Please note that the prices mentioned on this page: (a) present a range (depending upon the severity of the dental condition, the technology used in treatment, type of dental products used, etc.); (b) are true as on the date of this page and may change on a later date, in accordance with the standard company policy; (c) may be subject to standard aberrations or generalizations on account of the use of AI in general Google/internet search by you.Leave a Reply
Leave a Reply
Explore More Similar Posts
Explore More Blogs


Leave a Reply