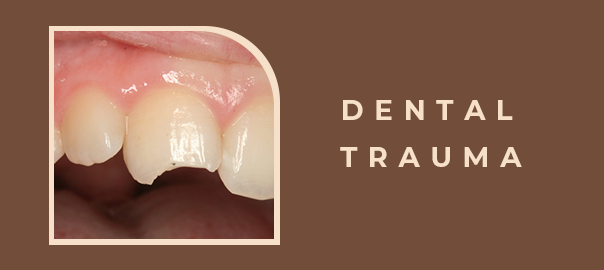
Dental Trauma – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
Dental trauma can be a distressing experience, causing pain and discomfort while potentially affecting your oral health. In this blog post, we will explore the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for dental trauma to help you better understand and manage these situations.
Symptoms of Dental Trauma
- 1. Pain and Discomfort:
One of the most common symptoms of dental trauma is pain, which can vary in intensity depending on the severity of the injury.
Discomfort may be felt while chewing or biting down, indicating damage to the affected tooth or surrounding structures. - 2. Swelling and Bruising:
Swelling and bruising around the injured area are typical signs of trauma. This may be accompanied by inflammation in the gums or cheeks - 3. Tooth Discoloration:
Discoloration of the affected tooth, ranging from slight changes to darkening, can occur due to internal bleeding or damage to the tooth pulp. - 4. Loose or Misaligned Teeth:
Trauma may lead to teeth becoming loose or misaligned. Immediate attention is crucial to prevent further complications. - 5. Bleeding Gums:
Injury to the gums may result in bleeding. It’s important to address this promptly to prevent infection.
Causes of Dental Trauma
- 1. Accidents and Falls: Trauma to the mouth can be caused by accidents, falls, or sports-related injuries, leading to a range of dental problems.
- 2. Biting on Hard Objects: Chewing on hard objects such as ice, pens, or popcorn kernels can cause fractures or chips in teeth.
- 3. Physical Altercations: Physical altercations, whether accidental or intentional, can result in dental trauma. It’s essential to seek professional help in such cases.
Treatment Options
- 1. Emergency Dental Care: Seek emergency dental care immediately after experiencing dental trauma. Timely intervention can prevent further damage and alleviate pain.
- 2. Tooth Splinting: In cases of loose or misaligned teeth, a dentist may use splints to stabilize and support the affected teeth while they heal.
- 3. Root Canal Therapy: If the dental pulp is damaged, a root canal procedure may be necessary to remove infected or damaged tissue and preserve the tooth.
- 4. Dental Crowns or Bridges: Dental crowns or bridges may be recommended to restore the shape and function of a damaged tooth.
- 5. Orthodontic Treatment: For misaligned teeth, orthodontic treatments such as braces or aligners may be suggested to correct the position over time.
Conclusion:
Dental trauma can happen unexpectedly, but prompt and appropriate care is crucial for a successful recovery. If you experience any symptoms of dental trauma, consult with a dentist promptly to assess the extent of the injury and determine the most suitable treatment plan for your situation. Remember, early intervention can make a significant difference in preserving your oral health and preventing long-term complications.
DISCLAIMER:Please note that the prices mentioned on this page: (a) present a range (depending upon the severity of the dental condition, the technology used in treatment, type of dental products used, etc.); (b) are true as on the date of this page and may change on a later date, in accordance with the standard company policy; (c) may be subject to standard aberrations or generalizations on account of the use of AI in general Google/internet search by you.Leave a Reply
Leave a Reply
Explore More Similar Posts
Explore More Blogs


Leave a Reply