Dental Abscess – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
Introduction
Dental abscesses are a common yet serious oral health issue that can cause significant pain and discomfort.
Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments is crucial for maintaining oral health. This blog provides detailed insights into dental abscesses and how to manage them effectively.
What is a Dental Abscess?
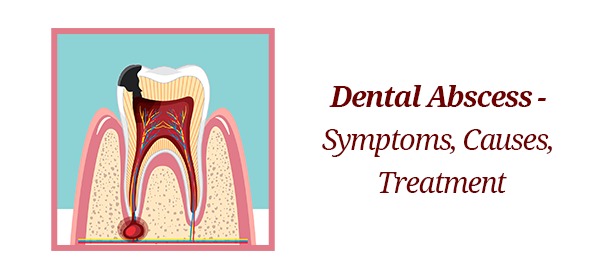
A dental abscess is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection. It can form in different parts of the tooth or gums and requires prompt treatment to prevent complications.
Common Symptoms of a Dental Abscess
Recognizing the symptoms of a dental abscess is key to seeking timely treatment. The most common symptoms include:
Primary Symptoms
1. Pain Manifestations
- Intense, throbbing tooth pain
- Pain radiating to jaw, neck, or ear
- Increased sensitivity to hot and cold
- Discomfort while chewing or biting
- Persistent toothache that worsens over time
2. Physical Changes
- Facial swelling, particularly around affected area
- Tender, swollen lymph nodes
- Gum inflammation and redness
- Visible bump or pimple on gums
- Tooth discoloration
Secondary Symptoms
- Bad breath or unusual taste
- Fever and general malaise
- Difficulty opening mouth
- Problems with swallowing
- Restless sleep due to pain
Ignoring these symptoms can lead to worsening conditions and more invasive treatments. Always consult a dentist if you notice any of these signs.
Causes and Risk Factors
Common Causes:
- Tooth Decay
- Gum Disease
- Cracked or Chipped Teeth
Risk Factors:
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing a dental abscess, including:
- Poor oral hygiene.
- High sugar intake.
- Dry mouth.
- Smoking.
Understanding these causes and risk factors can help you take preventive measures and lower your chances of developing a dental abscess.
Types of Dental Abscess
| Type | Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Periapical Abscess | Tip of the tooth root | Caused by untreated cavities or trauma. Bacteria invade the pulp, leading to pus formation. |
| Periodontal Abscess | Gums beside the tooth root | Often linked to gum disease. Bacteria accumulate in periodontal pockets. |
| Gingival Abscess | Surface of the gum tissue | Caused by foreign objects like food particles getting lodged in the gums, leading to localized pus. |
Treatment Options for Dental Abscess
1. Professional Interventions
- Immediate abscess drainage
- Antibiotic therapy for infection control
- Root canal treatment when applicable
- Tooth extraction in severe cases
- Professional cleaning and maintenance
2. Pain Management
- Prescribed pain medications
- Over-the-counter pain relievers
- Cold compress application
- Salt water rinses
- Temporary filling materials
3. Follow-up Care
- Regular dental check-ups
- Professional cleaning schedule
- Monitoring for recurrence
- Addressing underlying causes
- Preventive treatments
Complications of Untreated Dental Abscesses
Leaving a dental abscess untreated can result in severe complications, including:
- Bone loss around the affected area
- Spread of infection to other body parts
- Systemic infection risk
- Tooth loss
- Sinus complications
Prevention Tips
Preventing dental abscesses involves maintaining good oral health practices:
Daily Oral Care
1. Hygiene Practices
- Brush twice daily with fluoride toothpaste
- Floss at least once daily
- Use antimicrobial mouthwash
- Clean tongue regularly
- Replace toothbrush every 3-4 months
2. Dietary Considerations
- Limit sugary foods and drinks
- Avoid frequent snacking
- Drink plenty of water
- Choose tooth-friendly foods
- Consider sugar-free alternatives
Professional Care
- Regular dental check-ups
- Professional cleanings
- Early cavity treatment
- Prompt repair of damaged teeth
- Regular x-ray monitoring
Early intervention in dental issues like cavities or gum disease can significantly reduce the risk of abscess formation.
When to Seek Emergency Care
Immediate Attention Required If:
1. Severe Symptoms
- Difficulty breathing
- Severe swelling
- High fever
- Trouble swallowing
- Extreme pain
2. Spreading Infection Signs
- Facial swelling
- Neck stiffness
- Eye swelling
- Skin redness
- Mental confusion
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can a dental abscess heal without treatment?
No, dental abscesses require professional intervention. While symptoms might temporarily subside, the underlying infection remains active and can:
- Spread to surrounding tissues
- Lead to serious complications
- Cause permanent tooth damage
- Result in systemic health issues
- Require more extensive treatment if delayed
What’s the most effective way to treat a dental abscess?
The fastest and safest approach is professional dental care, which typically involves:
- Immediate abscess drainage
- Appropriate antibiotic therapy
- Treatment of the underlying cause
- Professional pain management
- Structured follow-up care
How can I prevent dental abscesses?
Prevention involves several key strategies:
- Practice thorough daily oral hygiene
- Schedule regular dental check-ups
- Address tooth decay promptly
- Maintain a balanced, low-sugar diet
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol
- Stay hydrated for optimal oral health
What are the danger signs requiring emergency care?
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Severe facial or neck swelling
- High fever with chills
- Extreme, uncontrolled pain
- Mental confusion or disorientation
Final Thoughts
Dental abscesses are serious oral health conditions requiring prompt professional attention. Regular dental check-ups and early intervention can help avoid severe complications and ensure long-term oral health.
Leave a Reply
Leave a Reply
Explore More Similar Posts
Explore More Blogs


Leave a Reply