Dental Abrasion – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
Are you facing heightened tooth sensitivity or observing alterations in the look of your teeth? You could be experiencing dental abrasion, a frequent issue in which your tooth enamel slowly diminishes. Continue reading to discover more about it!
In contrast to cavities, which result from bacteria, dental abrasion arises from regular mechanical forces that can impact anyone.
The positive aspect is that with adequate knowledge and attention, you can safeguard your teeth and handle this condition successfully.
What Is Dental Abrasion?
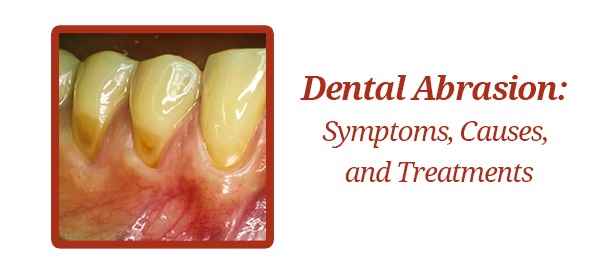
It refers to the gradual loss of tooth enamel caused by friction or mechanical wear.
This damage often occurs near the gumline or on the surface of teeth due to poor oral habits or environmental factors. The result can be visible grooves, increased sensitivity, and discoloration of the teeth.
Did You Know?
Tooth enamel is incredibly strong! But even after being the toughest substance in our body it cannot regenerate once it’s worn away. This makes early detection and prevention critical.
Symptoms of Dental Abrasion
Dental abrasion can manifest in several ways. Keep an eye out for these common symptoms:
- Tooth Sensitivity: Teeth may become more sensitive to hot, cold, or sweet foods and drinks due to exposed dentin.
- Visible Grooves or Notches: V-shaped indentations can form near the gumline.
- Thinning or Flattening of Teeth: Over time, teeth may appear less sharp or more worn down.
- Discoloration: Teeth can look yellow or brown as the underlying dentin becomes exposed.
Reasons for Dental Abrasion
Dental abrasion results from numerous activities and circumstances. Taking proactive measures prevents additional harm:
1. Bruxism (Grinding of Teeth)
Actions such as clenching or grinding teeth while sleeping frequently causes enamel erosion.
Teeth grinding is seen to be triggered by disruptions in sleep and elevated stress levels.
2. Conditions affecting the Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
TMJ problems can worsen bruxism and place uneven strain on teeth, leading to enamel erosion.
Brushing incorrectly
3. Excessive pressure or a toothbrush with hard bristles can wear away enamel.
Using a side-to-side technique instead of gentle circular motions can be detrimental.
Toothpaste with Scrubbing Qualities
4. Powerful abrasives found in toothpaste can slowly wear away enamel.
Always select toothpaste designed for sensitive teeth or marked as non-abrasive.
5. Foods and Beverages That Are Extremely Acidic
Citrus fruits and drinks such as sodas can weaken enamel, increasing its susceptibility to abrasion.
6. Chewing upon hard items
Enamel may slowly wear away if you bite on items such as pens, nails, or ice.
Understand the differences between Abrasion, Attrition, and Abfraction
| Feature | Abrasion | Attrition | Abfraction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mechanical wear of tooth enamel due to external factors (e.g., brushing). | Loss of tooth structure from tooth-to-tooth contact (e.g., grinding). | Loss of tooth structure due to stress or flexural forces at the tooth’s neck. |
| Causes | Overbrushing with hard bristles – Use of abrasive toothpaste – Chewing on hard objects |
Bruxism (teeth grinding/clenching) – Jaw misalignment |
Biting forces leading to flexion – Uneven distribution of chewing forces |
| Location on Teeth | Commonly near the gumline or on tooth surfaces | Occlusal (biting) surfaces | Cervical areas (near gumline) |
| Appearance | V-shaped notches, grooves, or thinning enamel | Flattened or worn-down biting surfaces | Wedge-shaped lesions near the gumline |
| Symptoms | Tooth sensitivity – Discoloration due to exposed dentin |
Tooth sensitivity – Loss of sharp tooth cusps |
Tooth sensitivity – Pain during biting or chewing |
| Treatment Options/strong> | Fluoride treatments – Tooth-colored fillings – Behavior modification (e.g., gentler brushing) |
Mouthguards for grinding – Orthodontic adjustments – Crowns or veneers for significant wear |
Restorative materials to fill defects – Address underlying biting forces |
Treatments for Dental Abrasion
Let’s break down your options for treating worn-down teeth. There’s actually quite a bit we can do!
Simple Changes That Make a Big Difference:
- Switch to a soft toothbrush. Always brush like you’re polishing a delicate surface – gentle circles do the trick.
- If you notice getting into the habit of grinding your teeth when asleep, mouthguards can be a real game changer for you.
- Watch out for those acidic foods and drinks – your teeth will thank you!
Professional Treatments That Help
1. Fluoride Power-Ups Your dentist can apply special fluoride treatments that make your teeth stronger and less sensitive. Think of it as armor for your teeth!
2. Tooth-Colored Repairs Got some grooves or notches? We can fill those in with materials that match your natural tooth color. Nobody will even notice!
3. Protective Shields For teeth that need extra help, crowns or veneers act like protective helmets, keeping your teeth safe and looking great.
When to See a Dentist
Your teeth are trying to tell you something if you notice:
- Deep grooves showing up where they shouldn’t be
- Wincing every time you sip something hot or cold
- Your jaw hurts in the morning, or your partner mentions you’re grinding your teeth at night
- Routine dental examinations are essential for identifying and addressing dental abrasion promptly.
FAQs
What does dental abrasion mean?
Dental abrasion refers to the erosion of tooth enamel. This most commonly results from physical forces, like vigorous brushing or grinding, instead of decay or injury.
Is it possible to reverse tooth abrasion?
No, enamel is incapable of regeneration. Nonetheless, therapies can enhance the look and performance of teeth while averting additional harm.
What is the method to address tooth abrasion?
Options for treatment consist of modifications in behavior, fluoride applications, fillings that match tooth color, and in serious instances, crowns or veneers.
What distinguishes abrasion from abfraction?
Abrasion occurs due to external mechanical forces, whereas abfraction stems from stress and flexing at the tooth’s neck, leading to wedge-shaped lesions.
Prevention Tips
Avoiding dental abrasion necessitates regular and attentive oral hygiene. Here are a few suggestions:
Brush Softly:
Utilize a toothbrush with soft bristles and apply gentle movements.
Select the Appropriate Toothpaste:
Fluoride toothpaste that is non-abrasive is best.
Reduce Acidic Foods:
Decrease consumption of foods such as citrus fruits and soft drinks.
Wear a Mouthguard:
Safeguard your teeth against grinding by utilizing a personalized mouthguard.
See the Dentist Frequently:
Regular examinations assist in detecting early indicators of wear and stopping advancement.
Final Thoughts
Let’s be honest – no one desires damaged teeth.
The positive update? You can halt dental abrasion immediately. It essentially comes down to properly caring for your teeth and visiting your dentist on a regular basis.
Consider it a way to invest in maintaining a bright and healthy smile for the future.
Helpful Hint: Make a note of when your teeth experience sensitivity or discomfort. Document what transpired that day – perhaps you used a new toothbrush or ate different meals. Such information is invaluable for your dentist. It assists them in determining precisely what is happening with your teeth and how to address it.
Leave a Reply
Leave a Reply
Explore More Similar Posts
Explore More Blogs


Leave a Reply