Dental Attrition – Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
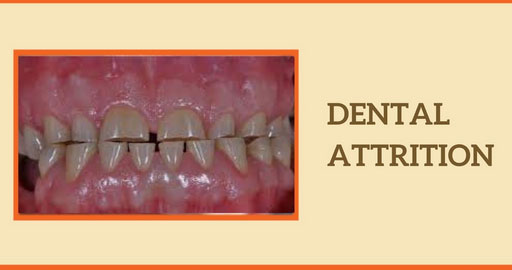
Dental attrition is a common condition seen in dentistry across all age groups. It refers to the gradual wearing down of tooth structure due to mechanical forces such as grinding, clenching, or constant tooth-to-tooth contact. In simple terms, attrition of teeth happens when enamel and dentin slowly wear away over time.
Understanding attrition in dentistry, its causes, and the right attrition treatment plan is essential to protect your teeth and prevent long-term damage.
Symptoms of Dental Attrition
The signs of attrition in teeth often develop gradually and may include:
- Tooth Sensitivity: When the enamel is worn away from your teeth, there can be an increase in sensitivity to the heat, cold, sweetness, or acidity of foods and drinks.
- Tooth Discoloration: It is known that the colour of the dentin itself is a yellowish shade; when enamel thins, it becomes more apparent, hence causing discoloration or a yellowish tint in the teeth.
- Chipped or Cracked Teeth: Weakened teeth, over some time, are bound to chip or crack, mostly at the edges.
- Change of Form: Friction will cause a change in form; thus, the teeth become flattened, wherein the edges are rounded.
- Pains and Discomforts: One will have pains in the jaw with associated headaches, even facial muscle strain from continuous grinding and clenching.
If left untreated, attrition teeth can affect both function and appearance.
Causes of Dental Attrition
Several factors contribute to attrition of teeth, including:
- Bruxism: The medical term for grinding teeth, which mainly occurs during sleep, is normally the result of stress, anxiety, or incorrect teeth alignment—malocclusion.
- Misaligned Teeth: Abnormal contact points develop when your teeth are misaligned, thus causing uneven wear and tear.
- Abrasive Diets: It can be caused by the consumption of highly abrasive food items and beverages. Chewing on ice, hard candy, or even using teeth as tools could further cause the erosion of enamel.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: In case good care is not taken for your teeth and gums, then it may result in growth of bacteria inside your mouth that form acids, which may break down the enamel of your teeth, thus making it weak and easily succumbing to attrition.
- Age: A certain amount of atrophy does occur with the wear and tear of aging normally. However, this becomes a bit of an issue when combined with other risk factors.
Treatment Options
The right dental attrition treatment depends on severity, cause, and the number of teeth involved. A personalized attrition treatment plan may include one or more of the following:
- Mouthguards: A custom-made dental night guard is a good deterring element for grinding teeth involuntarily because of bruxism. This simply creates a barrier between the upper teeth and the lower teeth, thereby preventing further damage due to grinding.
- Orthodontic Treatment: In the case of attrition caused by ill-aligned teeth, orthodontic procedures like braces or even clear aligners could help in realignment to prevent further abrasion.
- Dental Restorations: In cases where the attrition is leading to structural damage, then restorations to the tooth in the form of fillings, dental bridges and crowns, or veneers will have to be carried out to reinstate both functioning and esthetics.
- Lifestyle Changes: Stress and anxiety are the contributory factors of bruxism and can be treated using relaxation techniques or through therapy and exercise. With the reduction in the frequency and intensity of bruxism, erosion will reduce.
- Dietary Changes: The intake of abrasive foods should be reduced as far as possible. A balanced diet will not result in further erosion.
- Good Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing, flossing, and check-ups with the dentist are important for the application of stronger enamel and protection against dental attrition.
Dental Attrition Prevention
Backed by this view, some strategies on the prevention of dental attrition are well supported to minimise these forces and maintain tooth structures. Among them are the following:
- Regular dental checkups may help detect dental attrition earlier.
- Custom mouth guards protect teeth from grinding or clenching forces.
- Stress management techniques may help reduce bruxism-related tooth wear.
- Dietary adaptations such as avoiding hard or acidic foods prevent the erosion of the enamel.
- Good oral hygiene such as brushing and flossing maintains low plaque levels.
- This will avoid habits such as nail-biting that will lead to the wearing out of the teeth where necessary.
- Orthodontic treatment is carried out to align Class I malocclusion hence avoiding attrition.
- Fluoride treatment is done to strengthen the enamel against the erosion and wearing caused by acid.
- Avoiding too much acidic foods will reduce enamel erosion hence tooth wear. Professional cleaning removes plaque deposits hence minimising the risk for attrition.
When to see a doctor for attrition?
You should visit a dentist as soon as possible if you are suffering from dental attrition, with impending symptoms of worn and sensitive teeth, jaw pain, and altered bite. In doing so, the damage will be established, and the proper treatment or preventive measures can be designed.
Early diagnosis allows timely treatment of attrition, preventing the need for extensive restorations later.
Conclusion
The symptoms, causes, and treatment options regarding dental attrition are all significant in having a healthy and functional smile. In case you think you are losing because of dental attrition, you should visit cosmetic dentistry or consult a dental expert to decide upon the best treatment option that suits you best to save your teeth and oral health. By adopting a scientific manner of treatments, you can make sure that your smile lasts a lifetime and also your overall health. To know, you can BOOK AN APPOINTMENT.
FAQ’s
1. How to fix Dental Attrition?
The treatment of dental attrition would depend on how bad it is and what has caused the problem. It includes dental bonding, veneers, crowns, or orthodontic treatment, all of which might be done to restructure the tooth and achieve proper alignment of the bite. Preventive measures like mouthguards, managing stress, and a few diet modifications have to be administered.
2. What is the Difference between Dental Attrition and Bruxism?
Dental attrition is the wearing down of tooth structure by mechanical forces. Bruxism refers to the habit of clenching or grinding the teeth, mostly during sleep. Bruxism may cause dental attrition. However, dental attrition is not caused by bruxism in all cases.
3. Attrition rates for teeth:
Attrition rates differ in every individual because it is governed by individual habits, diets, oral hygiene habits, and pre-existing dental conditions. The factors, however advancing attrition are increasing age and other predisposing factors which are bruxism, malocclusion and acidic diet.
4. Can chewing gum cause attrition?
Moderate chewing sugar-free gum does not seem to have any significant attrition.
Leave a Reply
Leave a Reply
Explore More Similar Posts
Explore More Blogs


Leave a Reply