
Cavities: Everything You Need to Know About Tooth Decay and Treatment Options
Introduction
Did you know that even people who brush twice a day can still get cavities? Tooth decay is one of the most silent yet destructive oral health problems — it often starts without any symptoms and progresses quietly until real damage is done.
According to the World Health Organization, tooth decay is the most common non-communicable disease globally, affecting over 3 billion people. In India, national health surveys suggest that up to 84% of individuals may suffer from some form of dental cavities — yet only 6–10% seek timely treatment, especially when there’s no pain.
In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about cavities — from causes and symptoms to treatment options, preventive strategies (including for kids), and costs involved.
What Are Cavities?
Cavities, also known as dental caries or tooth decay, are permanent holes in your teeth caused by bacterial damage. They begin when bacteria in the mouth feed on sugars from food, releasing acids that gradually erode the tooth’s enamel.
How Cavities Form:
- Bacteria feed on sugars and release acids.
- Acids attack and weaken the tooth enamel.
- Over time, enamel dissolves and leads to discoloration and cavity formation.
Stages of Tooth Decay:
- Demineralization: Early stage where enamel starts breaking down (can be reversed with fluoride).
- Enamel Decay: Actual cavity forms on the enamel.
- Dentin Decay: Decay reaches the softer layer beneath enamel.
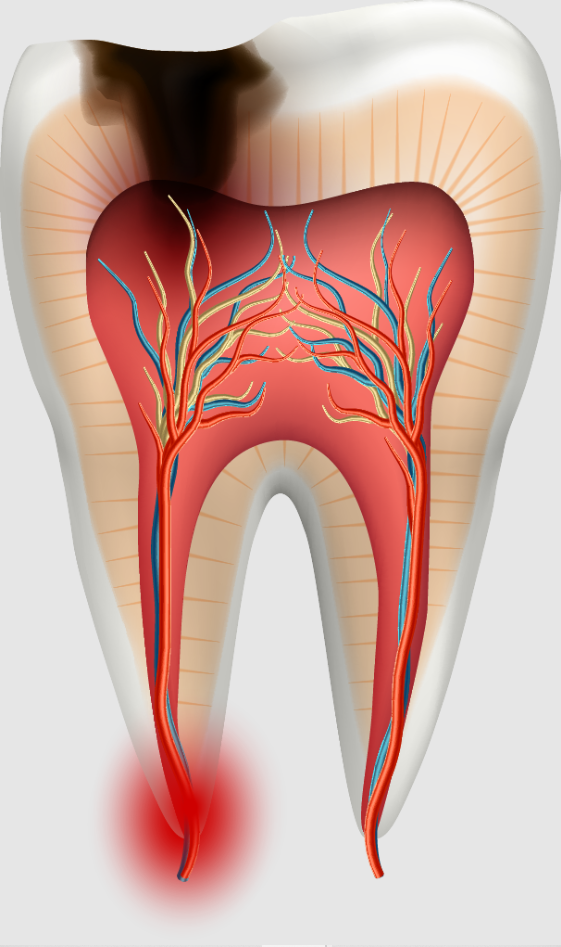
- Pulp Involvement: Infection spreads to the nerves and blood vessels, causing pain and inflammation.
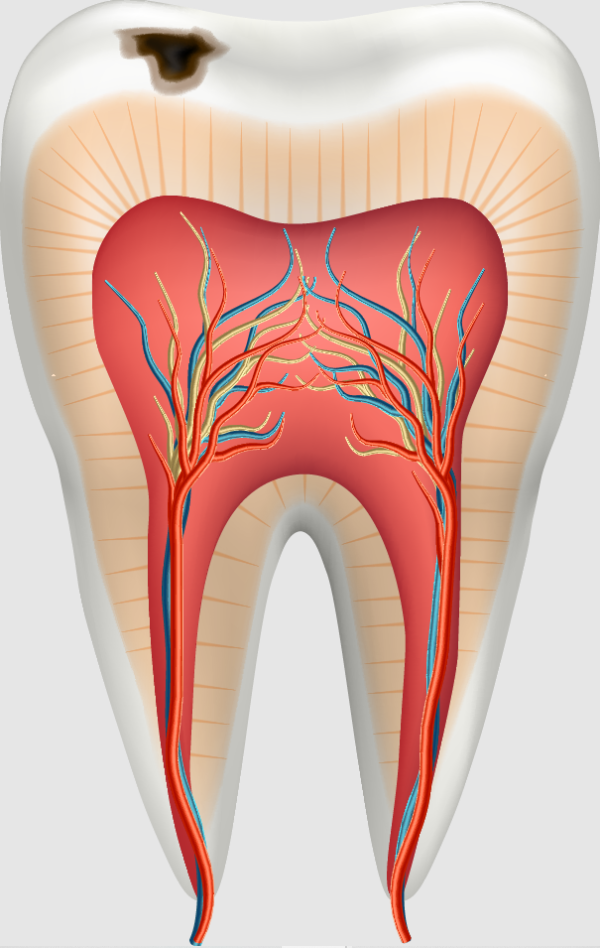
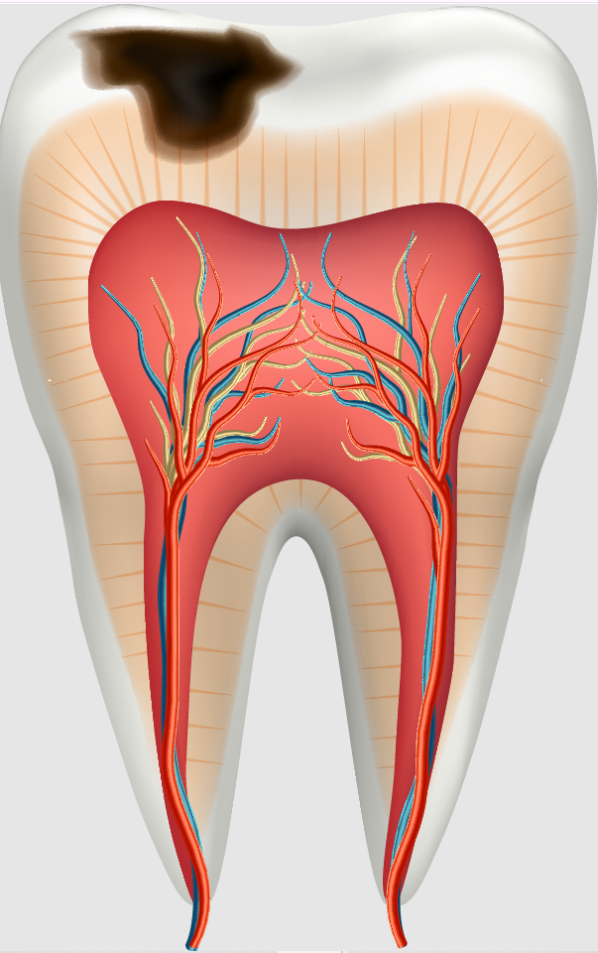
Symptoms of Cavities
Cavities may not cause pain initially, which is why routine dental checkups are essential. As decay progresses, symptoms become more noticeable.
 |
 |
 |
|
|
|
Causes of Cavities
Several everyday habits and biological factors contribute to the formation of cavities:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Irregular brushing & flossing or improper brushing technique leads to plaque buildup.
- Sugary & Acidic Diet: Frequent consumption of sugary foods or acidic drinks fuels harmful bacteria.
- Dry Mouth (Xerostomia): Reduced saliva means fewer natural defenses against bacteria.
- Bacterial Overload: Especially Streptococcus mutans, a common culprit.
- Genetics: Some people naturally have weaker enamel or more cavity-prone mouths.
- Medications and treatment: Certain medications that decrease salivary flow or alter the composition of saliva, or treatments such as cancer therapies, can disturb the secretion of saliva.
- Medical conditions: Sjogren syndrome, diabetes, eating disorders, Parkinsonism, which in one way or another affects the dynamic of saliva or as in Parkinsonism / cerebral palsy, individuals unable to maintain oral hygiene are more prone to develop dental cavities.
How Cavities Are Diagnosed
The course of dental cavities is unpredictable as it may go unnoticed without any symptom till it has caused extensive damage to the tooth or may present with obvious symptoms of sensitivity, pain, or food lodgement. Your dentist can best examine and diagnose cavities in the early stages, so we recommend a routine dental visit every 6months at least.
After taking a detailed history from the patient, dentists begin with a thorough oral examination, using a dental mirror to visually inspect teeth for discoloration, pits, or structural changes. If decay is suspected, they recommend an X-ray to assess the exact depth and extent of the lesion beneath the enamel. By combining insights from both the visual exam and radiographic imaging, the dentist develops a tailored treatment plan, selecting the most appropriate option based on the severity and location of the cavity.
Treatment Options for Cavities
Treatment depends on the cavity’s stage and severity:
Dental Fillings (Mild to moderate decay):
- Composite Fillings: Tooth-colored and ideal for front teeth.
- Glass Ionomer Cement (GIC) Fillings: Bonds chemically to tooth structure and releases fluoride to strengthen enamel.
Inlays, Onlays, or Pulp Capping (IPC/DPC) (Moderate decay with deeper involvement):
- Used when decay is too extensive for a filling but does not yet require a root canal.
Root Canal Therapy with Crown Placement (When decay reaches the pulp):
- Infected tissue is removed, and the tooth is sealed and restored with a crown to prevent further damage and restore function.
Tooth Extraction (Last resort):
-
- Done when the tooth is beyond repair.
How to Prevent Cavities
- Brush Twice Daily with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss Once a Day to clean between teeth.
- Use Antibacterial Mouthwash if recommended by your dentist.
- Limit Sugar and Acidic Food/Drinks.
- Stay Hydrated to support natural saliva production.
- Visit Your Dentist Twice a Year for professional cleaning and routine check ups.
- Remineralization varnishes for early white spot lesions.
Cavity Prevention in Kids
Children are especially vulnerable to cavities due to sugary diets and inconsistent hygiene habits.
Tips for Parents:
- Use toothpaste with fluoride levels recommended by your dentist appropriate for your child’s age.
- Ask your dentist about dental sealants to protect molars.
- Avoid bottle-feeding at bedtime with milk or juice.
- Educate kids on brushing and flossing as a daily routine.
Myths About Cavities
- Only kids get cavities: Not true. Adults and seniors are equally susceptible.
- If it doesn’t hurt, it’s not serious: Many cavities are painless in early stages and don’t hurt, but if left untreated, they will lead to terrible pain.
- Sugar is the only cause: Cavities are multifactorial; hygiene and genetics matter too.
- Brushing alone is enough: Without flossing and regular checkups, brushing won’t fully protect your teeth.
- No need to get milk teeth treated, they fall anyway: It is equally important to take good care of milk teeth as well because their premature fall leads to future orthodontic issues.
Cost of Cavity Treatment in India
Treatment costs (approximate) at Clove Dental: (cost varies depending on the number of tooth surfaces and areas involved)
|
Treatment Type |
Estimated Cost (INR) |
| Composite Fillings | ₹1,040 – ₹4,000 per tooth |
| Glass Ionomer Fillings | ₹1,040 – ₹4,000 per tooth |
| Root Canal Therapy | Starting at ₹5,790 per tooth |
| Crown Placement | Starting at ₹4,390 per tooth |
| Tooth Extraction | Starting at ₹1,000 |
FAQs
- Can cavities go away on their own?
No. Once enamel is damaged, a cavity cannot heal naturally; only early demineralization can be reversed with fluoride. - How long does a dental filling last?
Fillings typically last between 5 to 15 years, depending on the material used and your oral care habits. - Are home remedies effective against cavities?
Home remedies may help reduce bacterial load or freshen breath but cannot treat or reverse established cavities. - Is cavity treatment painful?
With modern techniques and the lack of pulp involvement, most cavity treatments are comfortable and virtually pain-free. Slight discomfort may be felt in cases where the cavity is approaching pulp. - When should I see a dentist?
Visit every 6 months for preventive care, and immediately if you notice pain, sensitivity, or visible changes in your teeth. - Why did I get a cavity despite daily brushing?
Brushing alone is not helpful. Your lifestyle, dietary habits, and genetics are all in control.
Final Word
Cavities may start small, but they can quickly become serious if ignored. With regular dental checkups, good oral hygiene habits, and a proactive approach to diet and prevention, you can significantly reduce your risk. Remember: noticing even a small spot or slight sensitivity warrants prompt attention to avoid more complex treatments later.
At Clove Dental, we’ve treated over 3 million patients across 650+ clinics pan India, offering expert diagnosis, personalized care, and a full spectrum of treatment options to help you maintain a healthy, cavity-free smile.
Leave a Reply
Leave a Reply
Explore More Similar Posts
Explore More Blogs


Leave a Reply